Carboxymethyl Cellulose
CAS:9000-11-7
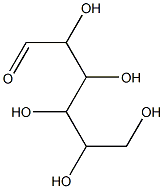
Molecular formula:C6H12O6
Molecular weight:180.15588
Structure:
Physicochemical properties: it is a non-toxic and tasteless white flocculent powder at room temperature. It has stable performance and is easily soluble in water. Its aqueous solution is neutral or alkaline transparent viscous liquid, soluble in other water-soluble adhesives and resins, and insoluble in organic solvents such as ethanol.
Application: carboxymethyl cellulose can form colloid and solution with high viscosity, which has the characteristics of adhesion, thickening, flow, emulsification and dispersion, shaping, water retention, colloid protection, film forming, acid resistance, salt resistance, suspension and other characteristics, and is physiologically harmless. Therefore, it is widely used in the production of food, medicine, daily chemicals, petroleum, papermaking, textile, construction and other fields. Its main uses: cigarette bonding, fabric sizing, shoemaking paste meal, household paste. The interior wall of the building is sprayed with imitation porcelain, mortar viscosity and concrete property. Molding and bonding of refractory fiber and ceramic production. The mud for oil drilling and exploration is thickened to reduce water loss. High quality paper surface sizing. Active additives for soap and detergent, as well as dispersion, emulsification, stability, suspension, film-forming, papermaking, polishing agents and so on in other industrial production. Among them, high-quality products can also be used in toothpaste, medicine, food and other industrial departments.
Carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) is a tackifier. It is a non-toxic and tasteless white flocculent powder at room temperature. It has stable performance and is easily soluble in water. Its aqueous solution is neutral or alkaline transparent viscous liquid, soluble in other water-soluble adhesives and resins, insoluble in ethanol and other chemical Book organic solvents. Carboxymethyl cellulose is the product of carboxymethyl group substitution of cellulose. According to its molecular weight or degree of substitution, it can be a completely soluble or insoluble polymer. The latter can be used as a weak acid cation exchanger to separate neutral or basic proteins.
IUPAC
acetic acid;2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxyhexanal
SMILES
CC(=O)O.C(C(C(C(C(C=O)O)O)O)O)O