Diuron
Product introduction: Substituted urea herbicides have internal absorption, conduction and certain contact killing effects. After being absorbed by plant roots or leaves, the agent inhibits photosynthesis, resulting in the loss of green leaves, discoloration of leaf tips and edges, and the death of plants due to lack of nutrition. Diuron can be weeded through potential difference and time difference at low dose. At high doses, it becomes a destructive herbicide. It is mainly used to control weeds in some plantations, such as tobacco, cotton, amaranth, etc.
CAS:330-54-1
Molecular formula:C9H10Cl2N2O
Molecular weight:233.09
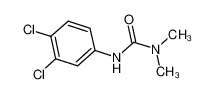
Structure:
Physicochemical properties: The pure product is a white crystalline solid. m. P. 158 ~ 159 ℃, vapor pressure 4.13 × 10-4Pa(50℃)。 Soluble in hot alcohol; At 27 ℃, the solubility in acetone is 5.3%; Slightly soluble in dioxane, ethyl acetate, ethanol and hot benzene; The solubility in water at 25 ℃ is 42mg / L. Stable in air, heated to 180 ~ 190 ℃, easy to decompose in case of strong acid and alkali, non corrosive and non flammable. Industrial products M.P. > 150 ℃.
Diuron, dicuron and ligulon are three commonly used substituted urea herbicides. Diuron is an internally absorbed and conductive herbicide with certain contact activity. It can be absorbed by plant roots and leaves, mainly by roots. After the weed roots absorb the agent, it is transmitted to aboveground leaves and spread around along the leaf veins, inhibiting the Hill reaction of photosynthesis, resulting in the loss of green leaves, The leaf tips and edges fade, turn yellow and die. Diuron can be used as a selective herbicide at low dose and as a destructive herbicide at high dose. Diuron is suitable for rice, cotton, corn, sugarcane, fruit, gum, mulberry and tea gardens, and can prevent and control barnyardgrass, horse Tang, dog tail grass, Polygonum, Chenopodium and eye vegetables.
IUPAC
3-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,1-dimethylurea
SMILES
CN(C)C(=O)NC1=CC(=C(C=C1)Cl)Cl