b

Thank You!
Your requirement has been sent, we will contact you quickly!
Sent Failed!
Try again!
Foreign name: lutein
Chemical formula: C40H56O2
Structural formula: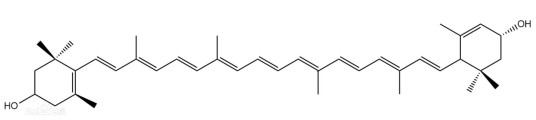
MW: 568.871
CAS accession number: 127-40-2
EINECS accession number: 204-840-0
Function:
Visual protective effect
Lutein is a type of fat soluble vitamin whose absorption spectrum contains near blue violet light that helps the eye's retina defend itself against UV light. For the eye, lutein is an important exerting antioxidant. Supplementation of a large amount of lutein to the human body helps to maintain visual persistence, improve visual response time, and reduce visual damage. For those who are myopic, lutein supplementation can delay the increase in their myopia severity.
pigmentation action
Xanthophylls are widely used in condiments, tobacco, pastries, Confectionaries, and multifeed processing. In China, xanthophyll hexyl is widely applied as a colorant.
Antioxidant effect
Oxygen free radicals in the human body are an important cause of many age-related pathologies, and lutein has strong antioxidant capacity, which is able to inhibit the activity of oxygen free radicals and prevent the destruction of normal cells by oxygen free radicals.
Anticancer effect
Lutein has unique biological efficacy in inhibiting tumor growth, the mechanisms of which mainly include antioxidant activity, inhibition of tumor vascular proliferation and cell proliferation, and so on.
Role of delayed early arteriosclerosis
The latest findings found that lutein can slow the development of early arteriosclerosis. After animal testing, it was found that the animals fed lutein and mouse chow, stirred together, and fed, had a lower incidence of arterial thrombosis than those not fed the diet containing lutein.
Role in diabetes prevention
Lutein may serve as an effective adjuvant to potentiate the hypoglycemic function of insulin. So eating foods like vegetables and fruits that are rich in Xanthophylls can reduce your risk of diabetes.

