Agrochemicals
Find
1814
related chemicals for you
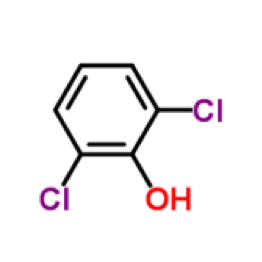
CAS:87-65-0
Molecular Formula:C6H4Cl2O
Alias
More Information
2,6-Dichlor-Phenol; 2,6-Dichlorfenol; 2.6-Dichlor-1-Hydroxy-Benzol; Phenol,2,6-Dichloro
Brief Introduction
2,6-dichlorophenol is a white crystalline solid with a strong odor. Odor threshold concentration: 0.003 mg/L at 86°F; 200 µg/L at 68-72°F. Taste threshold concentration: 0.0002 mg/L. (NTP, 1992)
2,6-dichlorophenol is a dichlorophenol with the chloro substituents at positions 2 and 6.
Suppliers
View More Vendors (5) >
CAS:88-73-3
Molecular Formula:C6H4ClNO2
Alias
More Information
2-Nitrochlorobenzene; Benzene, 1-Chloro-2-Nitro-; 1-Chloro-2-Nitrobenzene; O-Chloronitrobenzene; O-Nitrochlorobenzene (ONCB); ONCB
Brief Introduction
O-nitrochlorobenzene is an important intermediate in organic synthesis, and can be derived from many intermediates. It is used in the dye industry to make yellow GC, orange GR, etc; It is used to manufacture rubber accelerators m and DM in the aspect of additives; It is used in the synthesis of vanillin in the spice industry; Pesticide industry is used to produce tobuzin, methyltobuzin and carbendazim; It is also a raw material for benzotriazole ultraviolet absorbers. It is also an important intermediate of medicine.
Suppliers
View More Vendors (5) >
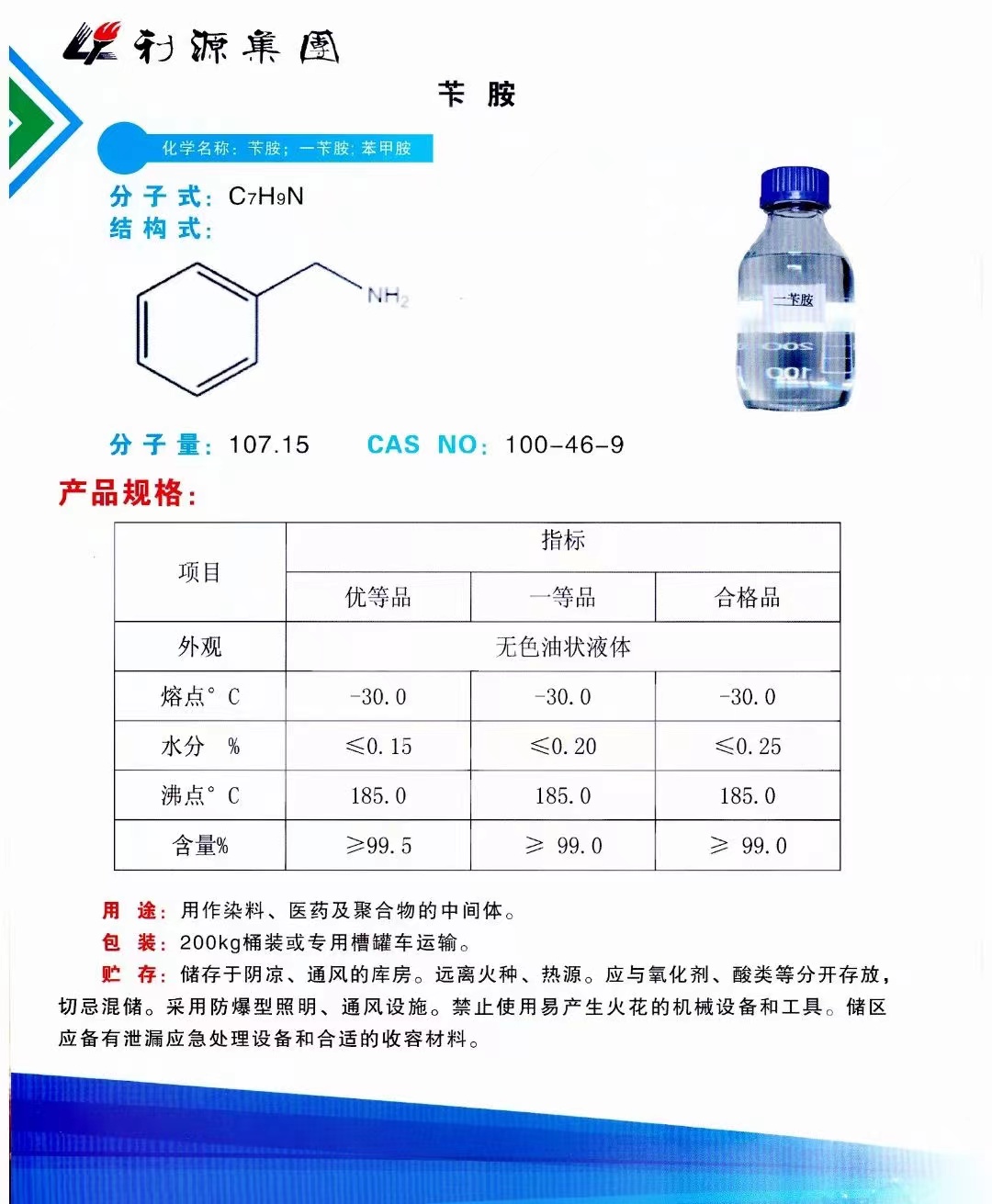
CAS:100-46-9
Molecular Formula:C7H9N
Alias
More Information
Phenyl-Methanamine; Phenylmethanaminium; Benzyl Amine; Phenylmethanamine; A-Aminotoluene; Benzylamin, (Acidimetrisch); Phenylmethylamine; Benzylamin; Benzenemethanamine; Moringine; Omega-Aminotoluene; Sumine 2005; Moringine[qr]; Omega-Aminotoluene[qr]; BZA
Brief Introduction
Benzylamine is a colorless liquid, which produces smoke in the air. It is miscible with water, ethanol and ether, and soluble in acetone and benzene. It can absorb CO2, react with halogenated hydrocarbon to form N-substituted benzylamine, react with acyl chloride, anhydride or ester to form n-benzylamide, and react with aldehyde and ketone to form n-benzylimine. It can be prepared by the reaction of benzyl chloride with ammonia, or by the reduction of benzonitrile, or by the reduction and ammoniation of benzaldehyde with NH3 and H2 / Ni. This product is used in organic synthesis, qualitative test of metal organic compounds, determination of platinum, vanadium and tungstate, and as precipitant of thorium, cerium, lanthanum and zirconium. Benzylamine is also an intermediate for the preparation of imidacloprid and acetamiprid, and is also an intermediate for sulfametholone.
Suppliers
View More Vendors (5) >
Anyang Lee Yuen New Materials Technology Co.,Ltd.
200KG/Drum
/
-
CAS:104-88-1
Molecular Formula:C7H5ClO
Alias
More Information
p-Chlorobenzaldehyde; 4-Chlorobenzaldehyde; p-Chlorobenzenecarboxaldehyde; Para-Chlorobenzaldehyde; P-Fluorobenzaldehyde; 4-Chlorbenzaldehyd; PARA Chloro Benzaldehyde; 4-Chloro Benzaldehyde; p Chloro Benzaldehyde
Brief Introduction
4-Chlorobenzaldehyde is also known as 4-chlorobenzaldehyde, with a molecular formula of C7H5ClO and a molecular weight of 140.567. This substance is mainly used in the manufacture of sedatives such as fenalol and aminophenolic acid and other pharmaceutical raw materials and intermediates. It is used in the manufacture of chlorocinnamon Aldehydes, weeding and killing enemies, etc.
Suppliers
View More Vendors (5) >
Hubei Lianchang New Material Co.,Ltd.
99.55%
/
Tech Grade
250kg
/
Plastic Drum
CAS:105-36-2
Molecular Formula:C4H7BrO2
Alias
More Information
Aceticacid,Bromo-,Ethylester; Bromo-Aceticaciethylester; Ethoxycarbonylmethyl Bromide; Ethyl Alpha-Bromoacetate; Ethyl Bromacetate; Ethyl 2-Bromoacetate; 2-Bromobutanoate; 2-Bromoacetic ACID Ethyl Ester; Ethyl Bromoacetate/Bromoacetic ACID Ethyl Ester; Ethylbromoacetate; 4-Methoxybenzyl Alcohol; Antol; Bromoacetic acid Ethyl Ester; Ethyl Monobromoacetate
Brief Introduction
Ethyl bromoacetate is used in organic synthesis, mainly in pharmaceutical and pesticide intermediates. It can also be used to make military poison gas.
Suppliers
View More Vendors (5) >

Enterprise standard
/
Tech Grade
25kg
/
Plastic Drum
Inquiry (
10
/ 10
)
Clear All
You can inquire for up to 10 products at a time
Sign In
Error!