CAS:6484-52-2
Molecular Formula:H4N2O3
Alias
More Information
Porus Prilled Ammonium Nitrate; NH4NO3
Brief Introduction
Ammonium nitrate, chemical compound ammonium nitrate, nitrate of ammonium, has the chemical formula NH4NO3, which is simplified to n2h4o3. It is a white crystalline solid and highly soluble in water. It is mainly used in agriculture as a high nitrogen fertilizer. The compound is used as a mining explosive and sometimes in improvised explosive devices. It is a popular explosive. The main component of explosives used in North America accounts for 80%.
Suppliers
View More Vendors (2) >
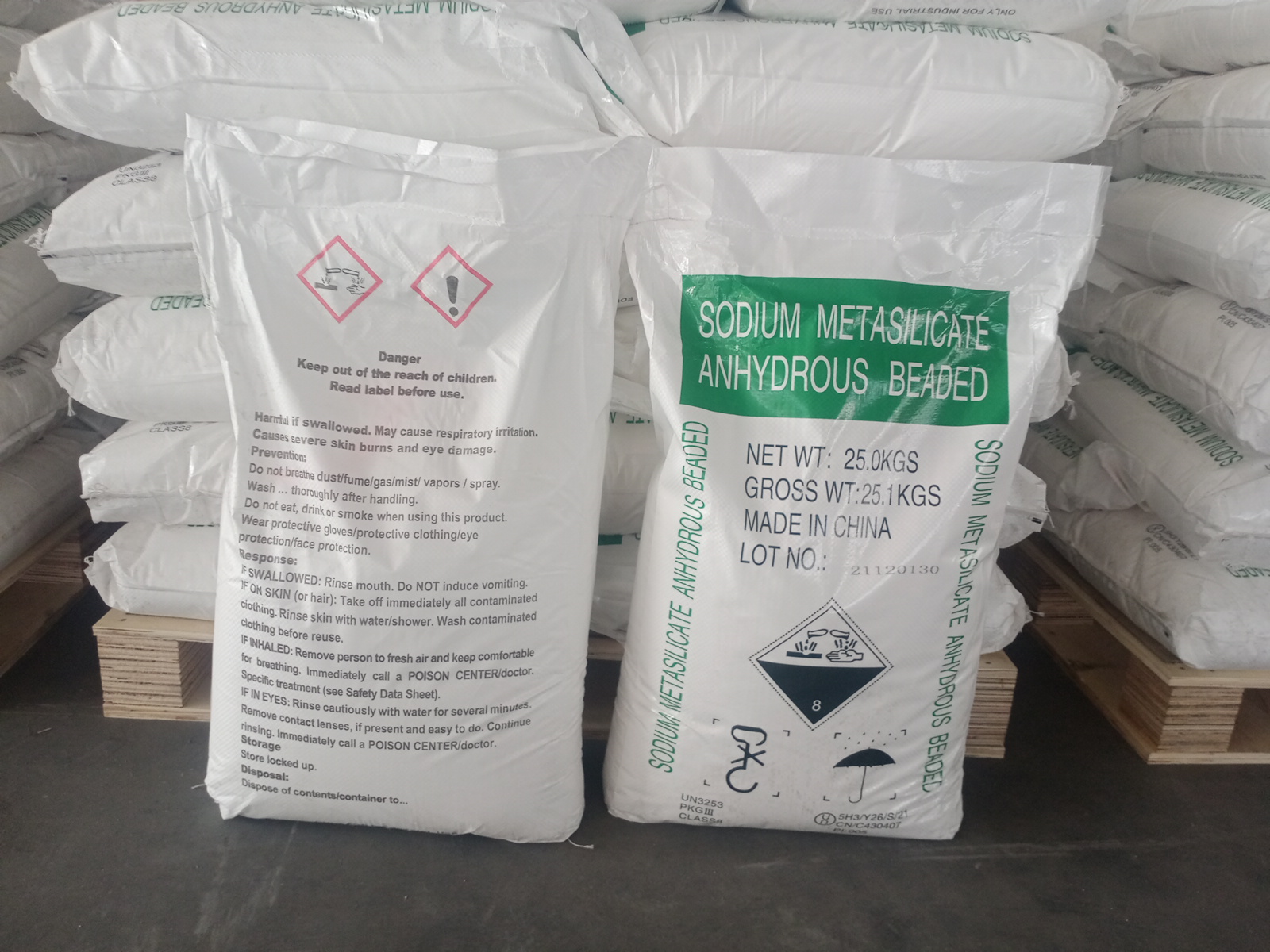
CAS:6834-92-0
Molecular Formula:Na2O3Si
Alias
More Information
Silica Standard; Sodium Sesquisilicate; Sodium Silicate, Meta; na2sio3; Sodium-M-Silicate; Sodium Metasilicate N-Hydrate; Water Glass; Disodium Trioxosilicate; Anhydrous Sodium Metasilicate; Sodium Metasilicate Anhydrous
Brief Introduction
It is used in the manufacture of detergent, fabric treatment agent and paper deinking agent
Suppliers
View More Vendors (2) >
CAS:7439-93-2
Molecular Formula:HLi
Alias
More Information
Lithium Metal; Lithium Rod; Litium; Lithium Ingot; Lithium Foil; Li; Litio; 3Li; Lithium Powder; Lithium Wire 3.2MM, 99.9%; Lithium Wire; Lithium
Brief Introduction
Lithium is a metal element with the element symbol Li. The corresponding elemental substance is silver white soft metal, which is also the metal with the lowest density. It is used in atomic reactors, light alloys and batteries. Lithium itself is not as polarizable as other lithium ions or alkali compounds, because lithium itself is not as polarizable as other lithium ions. This affects the stability of it and its compounds.
Suppliers
View More Vendors (2) >
Alias
More Information
Nickel Atom; Ni; Raney Nickle
Brief Introduction
Nickel is located in group 10 (VIII) and is the third element in the special triples (Fe, Co, Ni) of the first series of transition elements. Nickel is a hard, silvery white, malleable metal block or gray powder. Nickel powder is pyrophoric and can spontaneously ignite. It may react violently with titanium, ammonium nitrate, potassium perchlorate and hydrodicarboxylic acid. It is incompatible with acids, oxidants and sulfur. The chemical and physical properties of nickel, especially its magnetism, are similar to those of iron and cobalt. Some acids attack nickel, but it also provides good protection against air and sea water corrosion. This makes it very suitable for electroplating other metals to form a protective coating. Nickel is also an excellent alloy metal, especially iron, which can be used to make stainless steel and protective armor for military vehicles. It is extensible and can be drawn into lines. About a pound of nickel metal can be pulled to about 200 miles of thin wire.
Suppliers
View More Vendors (2) >
CAS:7440-05-3
Molecular Formula:Pd
Alias
More Information
Palladium; Palladium Powder; Pd; Palladium on Barium Sulfate; Palladium on Calcium Carbonate; Palladium on Alumina; Palladium on Charcoal; Palladium-Activated Carbon; Palladium Charcoal
Brief Introduction
It is mainly used for thick film paste in electronic industry and inner and outer electrode materials of multilayer ceramic capacitors; It is also used in the manufacture of dental materials, watches and surgical instruments; Used for preparing catalysts (palladium coated asbestos, sponge palladium, etc.), low current contact points, printed circuits, alloys for clocks and watches, etc; Used for electrical instruments, precision alloys, etc; Electrical instruments, chemical industry and manufacturing precision alloys.
Suppliers
View More Vendors (2) >
Inquiry (
10
/ 10
)
Clear All
Sign In
Error!