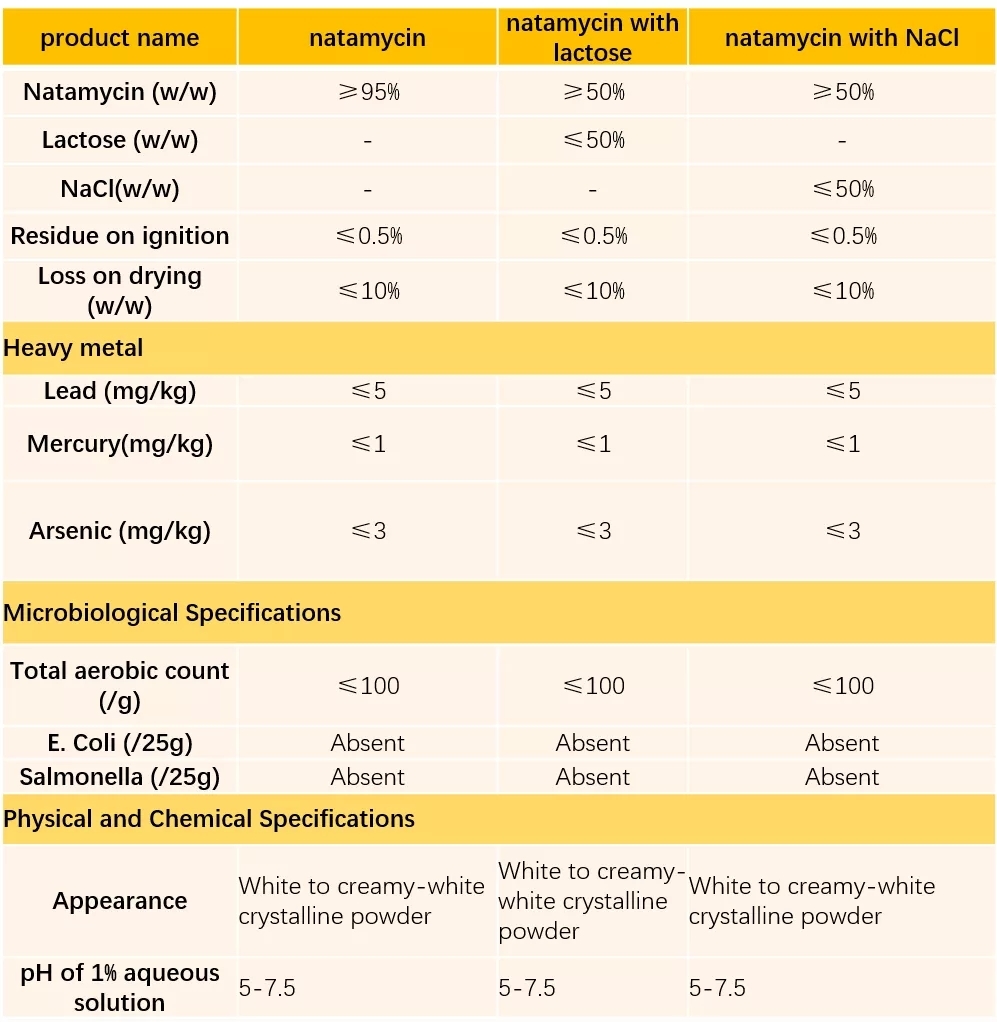
Natamycin
The deterioration of food caused by thegrowth of mold not only affects the color, aroma, and taste of the product, butsome mycotoxins produced by some molds seriously affect the life and health ofconsumers.
Natamycin is a natural antifungal compound produced by the fermentation of Streptomyces. Under a verysmall amount of use (usually 5-10PPM) , it can effectively inhibit the growthof various molds and yeasts, and also inhibit the production of mycotoxins. Therefore,natamycin could effectively extend the food shelf life and retain the food quality without any side effects on human intestinalflora. It is listed as one of only three bio-type food preservatives approved by the state. In usage, Natamycin has no inhibitory effect on bacteria, so itdoes not affect the natural ripening process of yogurt, cheese, raw ham, anddried sausages.
Mechanism
Natamycin relies on its lactone ring structure to interact with sterol compounds on thefungal cell membrane to form antibiotic-sterol compounds, thereby destroying the structure of the fungal cell membrane. The hydrophilic part (polyol part) of the macrocyclic lipid forms water pores in the membrane, impairs the permeability of the cell membrane, which in turn causes substances such as amino acids and electrolytes in the bacteria to ooze out and the cells die.
Potency
Even though the bacteriostasis of Nataymicin is highly targeted, it can effectively inhibit the growth and reproduction of almost all kinds of molds and yeasts, and can inhibit the production of mycotoxins at very low dose.
The pure natamycin has a very low solubility in water, which make it not easy penatrate the surface of the food, especially bakery product; this characteristic enhance the anti-mold effect of natamycin.
Unlike other antimicrobial products used in food, Natamycin can play a very good antiseptic and fresh-keeping effect in the range of pH3-9 , which makes it suitable for all kinds of acidic , neutral and slightly alkaline foods.
Safe and Natural
Natamycin is a natural product produced during the fermentation of Streptomyces. After entering the human body, it is not absorbed by the body and is directly eliminated from the body, because it does not affect the health of the consumer and the intestinal flora.
Packaging
500g/bottle×10 bottles/carton, 500g/bag×20bag/carton, 20kg barrel,
can be customized according to customerrequirements
Storage
It should be stored in a cool, dryand well-ventilated warehouse
Shelf-life
Under the condition of 0-10℃, the shelflife is 24 months
Applications
Cheese, pastries, stewed meat products,smoked, roasted, barbecued meat, fried meat, Western ham, meat enema, fermentedmeat products, mayonnaise, salad dressing, fruit and vegetable juice (pulp),fermented wine
Usage
Direct addition or surface treatment(spraying or soaking of suspension), the recommended amount is 0.01-0.3g/kg

Natamycin has a strong inhibitory effect on molds, yeasts and fungi, but has no inhibitory effect on bacteria, viruses and other microorganisms. Natamycin has a certain heat treatment resistance, relatively stable in dry state, and can withstand short-term high temperature (100 ℃); However, it is not suitable to contact with sunlight because of its ring chemical structure and sensitivity to ultraviolet rays. The anchor stability of natamycin activity is affected by pH value, temperature, light intensity, oxidants and heavy metals, so the product should avoid contact with oxides and hydrogen sulfide compounds. In June 1982, the FDA officially approved natamycin as a food preservative and classified it as gras products. Natamycin is a highly effective inhibitor of mold, yeast and fungi. It is used to inhibit mold, yeast and fungi in food. It is very safe and reliable to human body, and does not affect the flavor of products. It is widely used in cheese, meat products, cakes, fruit juice and other foods all over the world. The product is refined from streptomycin by deep fermentation and multi-step extraction process. The preparation is made by mixing 50% natamycin and 50% lactose.
IUPAC
(1R,3S,5R,7R,8E,12R,14E,16E,18E,20E,22R,24S,25R,26S)-22-[(2R,3S,4S,5S,6R)-4-amino-3,5-dihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy-1,3,26-trihydroxy-12-methyl-10-oxo-6,11,28-trioxatricyclo[22.3.1.05,7]octacosa-8,14,16,18,20-pentaene-25-carboxylic acid
SMILES
CC1CC=CC=CC=CC=CC(CC2C(C(CC(O2)(CC(CC3C(O3)C=CC(=O)O1)O)O)O)C(=O)O)OC4C(C(C(C(O4)C)O)N)O