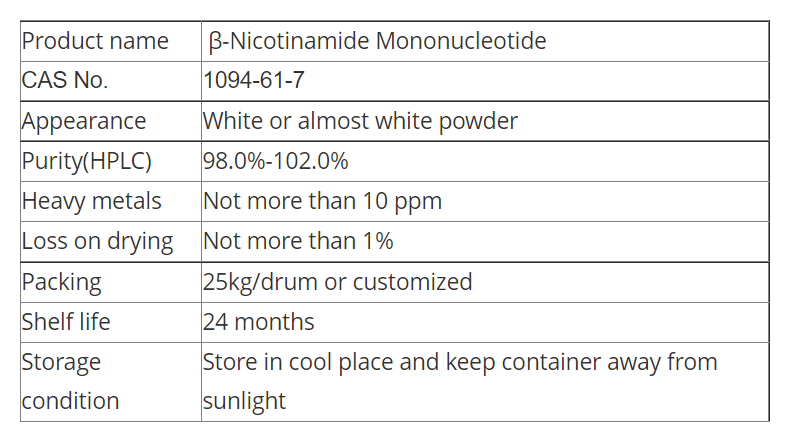
β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide
CAS No.: 1094-61-7
Molecular formula: C11H15N2O8P
Application:
APIs, intermediates, health products, cosmetics
Product introduction:
Nicotinamide mononucleotide plays an important role in human cell energy production. It participates in the synthesis of intracellular NAC (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, an important coenzyme of cell energy conversion). Nicotinamide is a derivative of vitamin B3. NAD + is a molecule with multiple functions in vivo, which is mainly realized by promoting cell signal transduction enzymes called sirtuins. These enzymes are essential for normal function, among which s1rt1 (with seven silent regulatory proteins) is particularly unique. Studies have shown that it has high activity after caloric restriction, and caloric restriction itself brings many benefits, including signs of life extension. There is no doubt that further tests show that the increase of s1rt1 level can prevent metabolic decline and disease.

Is it safe to take NMN for a long time?
NMN itself is a natural substance in the human body and also exists in many foods. It is pure natural and harmless. Studies have confirmed that NMN supplementation will not affect the activities of various enzymes in the supplementary synthesis pathway, and oral Nampt, PARP, Nmnat and other activities have no effect, which directly changes the level of NAD + in vivo.

The research shows that the elderly over 65 years old with about 70kg should supplement about 600mg NMN every day, and the young people aged about 45 should supplement about 300mg. This is equivalent to eating about 32g of soybeans or broccoli every day, or under the condition of ensuring complete absorption. Of course, this can not be achieved at all. Therefore, it is particularly important to supplement NMN from non food sources.
Nicotinamide mononucleotide ("NMN" and "β-NMN") is a nucleotide derived from ribose and nicotinamide. Niacinamide (nicotinamide,) is a form of vitamin B3 (niacin.) As a biochemical precursor of NAD+, it may be useful in the prevention of pellagra.
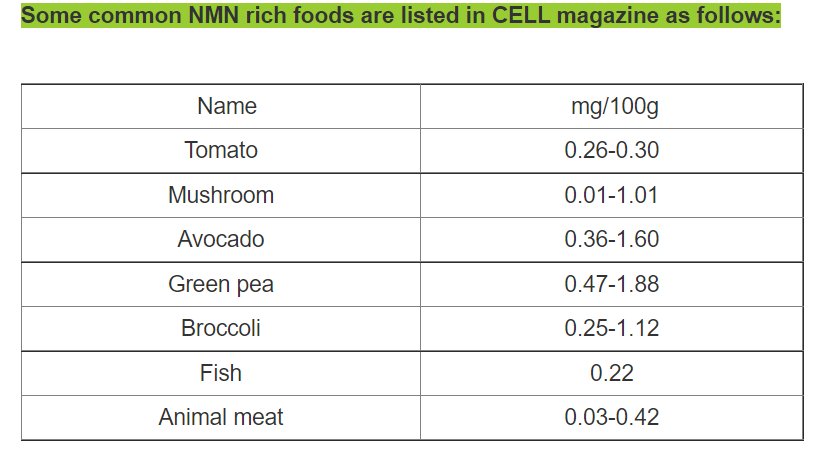
Its unconcentrated form, niacin, is found in a variety of nutritional sources: Peanuts, Mushrooms (portobello, grilled), Avocados, Green Peas (fresh), and certain fish and animal meats.
In studies [on mice], NMN has shown to reverse age-related arterial dysfunction by decreasing oxidative stress.
The anti-ageing properties will be tested on humans in July 2016.
IUPAC
[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(3-carbamoylpyridin-1-ium-1-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methyl hydrogen phosphate
SMILES
C1=CC(=C[N+](=C1)C2C(C(C(O2)COP(=O)(O)[O-])O)O)C(=O)N