b

Thank You!
Your requirement has been sent, we will contact you quickly!
Sent Failed!
Try again!
Introduction:
Vitamin C, also known as L-ascorbic acid, is an essential nutrient for higher primates and a few other organisms. Ascorbic acid can be produced by metabolism in most organisms, but humans are the most significant exception. The most well-known is that lack of vitamin C can cause scurvy. The pharmacodynamic group of vitamin C is ascorbic acid ion. In organisms, vitamin C is an antioxidant because it can protect the body from oxidants. Vitamin C is also a coenzyme.
Physical and chemical properties:
Vitamin C is easily soluble in water, slightly soluble in ethanol, insoluble in ether, chloroform, benzene, petroleum ether, Oils and fats. The aqueous solution shows acidic reaction. It can be quickly oxidized into dehydroascorbic acid in the air, with citric acid like acidity. It is a strong reducing agent, which gradually turns into different degrees of light yellow after long storage. This product exists in all kinds of fresh vegetables and fruits. This product plays an important role in biological oxidation and reduction and cell respiration. It is conducive to nucleic acid synthesis and promote the formation of red blood cells. It can also reduce Fe3 + to Fe2 +, which is easy to be absorbed by the human body and is also beneficial to the formation of cells.
CAS:50-81-7
Molecular formula: C6H8O6
Molecular weight: 176.12
Structural type: 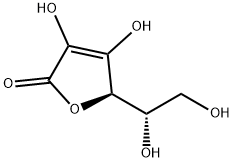
Purpose:
Vitamin C participates in the production of collagen in the body, neutralizes toxins and promotes the production of antibodies, which can enhance the detoxification function of the body. In medicine, it is mainly used for the prevention or treatment of scurvy, and for dental caries, gingival abscess, anemia, growth and development stagnation and other diseases caused by ascorbic acid deficiency. In food processing, it is used as vitamin fortifier for concentrated orange juice, fruit juice crystal, candy, jelly, jam, etc.

